Diagnosis and Treatment of Furcation-Involved Teeth: A Comprehensive Guide

Furcation-involved teeth present a significant challenge for dental professionals due to their complex anatomy and the challenges associated with accessing and treating the affected areas. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth examination of furcation-involved teeth, encompassing their causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and a wide range of treatment modalities. Through the exploration of advanced techniques, case studies, and expert insights, this guide empowers dental practitioners with the knowledge and skills to effectively manage these complex cases, ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 21754 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 289 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Causes and Symptoms of Furcation Involvement
Causes
Furcation involvement typically arises from periodontal disease, a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the supporting structures of the teeth. When periodontal disease progresses, it can lead to the destruction of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone, exposing the furcation area. Other factors that may contribute to furcation involvement include:
- Carious lesions extending below the cementoenamel junction
- Iatrogenic factors, such as over-instrumentation during root canal treatment or periodontal surgery
- Anatomical variations, such as root concavities or furcation grooves
- Occlusal trauma or excessive forces on the teeth
Symptoms
Furcation involvement can manifest in various ways, including:
- Periodontal probing depths greater than 5 mm in the furcation area
- Bleeding on probing or spontaneous bleeding from the furcation
- Gingival recession exposing the furcation
- Bone loss visible on radiographs
- Tooth mobility or sensitivity
- Pain or discomfort upon chewing
Diagnosis of Furcation Involvement
Accurate diagnosis of furcation involvement is crucial for devising an appropriate treatment plan. This involves a thorough clinical examination, including periodontal probing, radiographic assessment, and appropriate diagnostic tests.
Clinical Examination
Clinical examination involves careful assessment of the furcation area using a periodontal probe. Probing depths greater than 5 mm, bleeding on probing, or the presence of a furcation groove or concavity may indicate furcation involvement.
Radiographic Assessment
Radiographs, such as periapical and bitewing views, provide valuable information about the extent of bone loss and the relationship between the furcation and surrounding structures. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) may also be utilized for more detailed evaluation of complex cases.
Diagnostic Tests
Additional diagnostic tests may be employed to confirm furcation involvement and assess the vitality of the tooth. These tests may include:
- Vitality testing using electric pulp tester or cold sensitivity test
- Transillumination to detect root fractures or perforations
- Laser Doppler flowmetry to evaluate blood flow in the furcation area
Treatment of Furcation-Involved Teeth
The treatment approach for furcation-involved teeth depends on several factors, including the severity of the involvement, the presence of other complicating factors, and the patient's overall health status. The primary goals of treatment are to eliminate infection, restore function, and prevent further tooth loss.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment options for furcation-involved teeth focus on controlling infection and inflammation. These may include:
- Scaling and root planing to remove plaque and calculus from the root surfaces
- Antibiotic therapy to eliminate bacterial infection
- Occlusal adjustment to reduce excessive forces on the teeth
- Periodontal maintenance to prevent disease recurrence
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment is indicated when non-surgical approaches fail to resolve the infection or restore function. Surgical procedures for furcation-involved teeth may include:
- Flap surgery to access the furcation area for debridement and root surface instrumentation
- Guided bone regeneration (GBR) to promote bone growth in the furcation defect
- Root amputation to remove a portion of the tooth root that is severely compromised
- Crown lengthening to expose more of the tooth structure for restorative purposes
Advanced Techniques in the Management of Furcation-Involved Teeth
Recent advancements in dental technology and materials have led to the development of innovative techniques for the management of furcation-involved teeth. These techniques include:
- Laser therapy to disinfect the furcation area and promote tissue healing
- Ultrasonic instrumentation to remove calculus and biofilm from the root surfaces
- Micro-air abrasion to remove caries and expose sound tooth structure
- Bioactive materials to promote bone regeneration and improve wound healing
These advanced techniques offer minimally invasive and more effective approaches to the treatment of furcation-involved teeth, enhancing patient outcomes and improving the long-term prognosis.
Case Studies
Clinical case studies provide valuable insights into the diagnosis and treatment of furcation-involved teeth. These cases demonstrate the application of various treatment modalities and the challenges encountered in managing complex clinical scenarios.
Case 1
A 45-year-old patient presented with a furcation-involved mandibular molar. The tooth had deep periodontal pockets, bleeding on probing, and radiographic evidence of bone loss. Non-surgical treatment, including scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, and occlusal adjustment, failed to resolve the infection. Surgical intervention was performed, involving a flap procedure, debridement, and guided bone regeneration. The tooth was successfully restored to function, and the patient experienced significant improvement in periodontal health.
Case 2
A 32-year-old patient presented with a furcation-involved maxillary premolar. The tooth had a deep carious lesion extending below the cementoenamel junction. Root canal treatment was performed, but the infection persisted due to the involvement of the furcation area. A surgical approach was employed, involving a root amputation to remove the severely compromised portion of the root. The remaining root structure was restored with a crown, and the patient achieved a favorable outcome.
Furcation-involved teeth present unique challenges for dental professionals. However, with a thorough understanding of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, clinicians can effectively manage these complex cases. This comprehensive guide has explored the intricacies of furcation involvement, from its diagnosis to the latest treatment strategies. By embracing advanced techniques and leveraging case studies, dental practitioners can enhance their skills and improve patient outcomes, ensuring the preservation of furcation-involved teeth and the maintenance of oral health.
If you are experiencing symptoms of furcation involvement, it is crucial to seek professional dental care promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis and prevent further tooth damage.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 21754 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 289 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Allen C Guelzo
Allen C Guelzo Carol Tuttle
Carol Tuttle Rahele Jomepour Bell
Rahele Jomepour Bell Dr Sally Carruthers
Dr Sally Carruthers Donna Scholefield
Donna Scholefield Nolan Hester
Nolan Hester Austin Rogers
Austin Rogers Michael Wakefield
Michael Wakefield Barbara R Krasner
Barbara R Krasner Jenny Mccarthy
Jenny Mccarthy Keith William Nolan
Keith William Nolan Joel T Dudley
Joel T Dudley Lori Nordstrom
Lori Nordstrom Philip K Dick
Philip K Dick James C Galvin
James C Galvin Erick C Jones
Erick C Jones Kathy Collard Miller
Kathy Collard Miller Robert Condon
Robert Condon Antoine Faivre
Antoine Faivre Carter Lindberg
Carter Lindberg
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Chadwick PowellThe Urban Contract: How Community Governance and Capitalism Can Coexist and...
Chadwick PowellThe Urban Contract: How Community Governance and Capitalism Can Coexist and... Ernest ClineFollow ·2k
Ernest ClineFollow ·2k Terence NelsonFollow ·11.6k
Terence NelsonFollow ·11.6k Harry CookFollow ·15.3k
Harry CookFollow ·15.3k John UpdikeFollow ·15.9k
John UpdikeFollow ·15.9k Edison MitchellFollow ·18.8k
Edison MitchellFollow ·18.8k Harrison BlairFollow ·11.9k
Harrison BlairFollow ·11.9k Stuart BlairFollow ·19.6k
Stuart BlairFollow ·19.6k Esteban CoxFollow ·4.8k
Esteban CoxFollow ·4.8k

 Henry Green
Henry GreenCorrosion and Its Consequences for Reinforced Concrete...
Corrosion is a major threat to reinforced...

 James Gray
James GrayDiscover the Enigmatic World of Pascin in "Pascin Mega...
Immerse Yourself in the...

 George R.R. Martin
George R.R. MartinUnlocking the Power of Nature: Delve into the Bioactive...
In a world increasingly...

 Julian Powell
Julian PowellMaster the Art of Apple Watch App Development: A...
Unlock the Potential of Apple Watch Apps In...
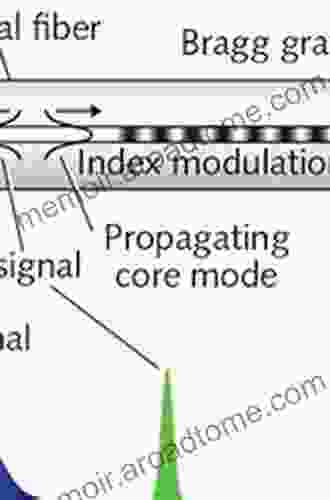
 Jaylen Mitchell
Jaylen MitchellPlastic Optical Fiber Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide to...
In the rapidly evolving landscape of...

 Truman Capote
Truman CapoteUnlock the Secrets of Language Creation: Dive into...
The realm of computer science...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 21754 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 289 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |